Mutual Funds Classification
A mutual fund is a professionally managed financial instrument that pools money from many investors to purchase securities such as stocks, bonds, money market instruments, etc. It offers more diversification and opportunity for investors to make smart investments without being actively engaged in the day to day investment activities.
Advantages of investing in mutual funds include:
- Built-in diversification - Mutual Funds invest in a wide range of securities which helps offset the impact of poor performers, while taking advantage of the earning potential of the rest.
- Professional Management - Mutual Funds are run by qualified and professional fund managers who actively track their funds and re-balance the portfolios from time to time as new information comes in.
- Fulfils various investment objectives - Mutual funds can be used to meet various financial goals. For example:
- ELSS funds for tax planning
- Diversified equity funds for long term wealth creation
- Debt mutual funds for stable returns and preservation of capital
- Liquidity - For open-ended funds, you can redeem all or part of your investment any time you wish and receive the current value of the investments. However, it is important to watch out for lock-in period and exit load fees.
- Regulations - All mutual funds are required to register with SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India). They are obliged to follow strict regulations designed to protect investors. All operations are also regularly monitored by SEBI.
Mutual funds can be classified as follows:
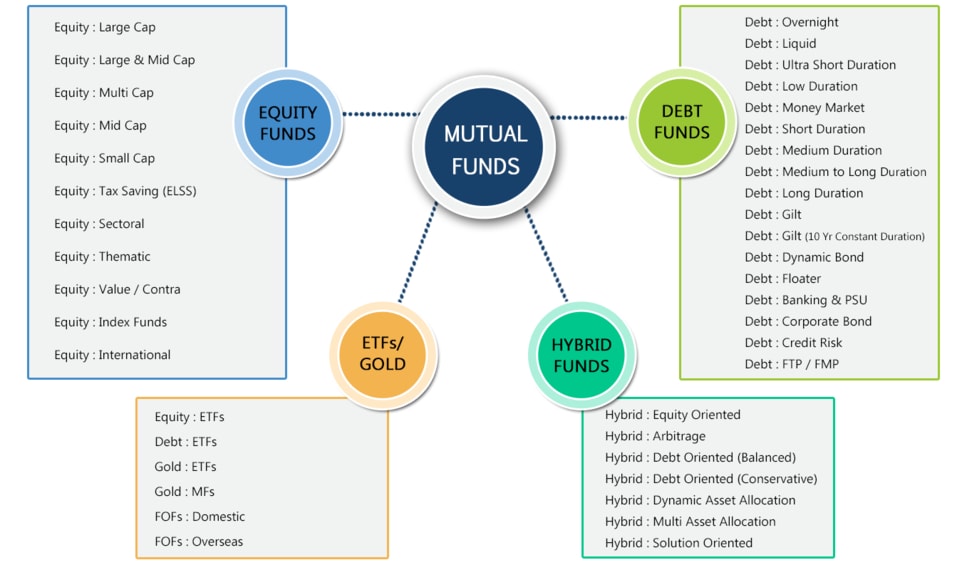
Types of Mutual Funds
An equity fund is a mutual fund that invests primarily in stocks. In this way, the investor is able to buy a basket of stocks more easily than buying individual stocks and the investor also reaps the benefits of a diversified portfolio. Equity funds have historically provided the highest rate of return but are also more volatile as they are market dependent. Although, equity funds can generate outstanding returns in a short span of time as well, but investors should ideally have a long term time frame to counter volatility.
Equity funds can be further classified as:
According to market capitalization
It is a measure by which we can classify a company’s size. It is the current market value of the company’s outstanding shares.
- Large Cap Funds: When a larger proportion (>=80%) of the portfolio is invested in stocks of companies with large market capitalization.
- Large & Mid Cap Funds: These funds will invest in both large cap and midcap stocks. The funds would invest at least a minimum of 35 per cent in large cap companies and 35 per cent in mid cap companies.
- Multi Cap Funds: These funds will invest in stocks across large, mid, small market capitalization. The funds would invest at least a minimum of 25 per cent in large cap companies, 25 per cent in mid cap companies and 25 percent in small cap companies.
- Flexi Cap Funds: Flexi Cap Mutual Fund is an open-ended, dynamic equity scheme that invests across various market capitalizations i.e large-caps, mid-caps, and small-caps without any fixed allocation requirement as in multi-cap funds. The minimum investment in equity and equity-related instruments needs to be 65% of the total assets of the scheme.
- Mid Cap Funds: When 65% or more of the portfolio is invested in stocks of mid and small size companies. They are usually more volatile than large cap funds.
- Small Cap Funds: When 65% or more of the portfolio is invested in stocks of small size companies. Amongst all equity funds, they are the most volatile but have also provided the highest return over long holding periods.
ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme) Funds
ELSS funds, also known as tax saving mutual funds, are diversified equity funds with a lock-in period of 3 years. They offer tax benefits u/s 80C up to Rs.1,50,000.
Sectoral Funds
These funds invest predominantly (>=80%) in businesses that operate in a particular industry or sector of the economy. Since the overall market may alternate between favouring different sectors, these funds benefit investors with a deep understanding of a particular sector’s potential.
For example: Pharmaceuticals, Financial Services, Technology, etc.
Thematic Funds
A thematic fund is a broad-based investment style. It identifies a theme and then invest in companies that are united by the theme. The theme could be investing in companies with high dividend yields, investing in MNCs (multi-national companies), etc. Minimum 80% of the fund is invested in a particular theme.
For example: Consumption, MNCs, etc.
Value / Contra Funds
Value funds follow a value investing strategy and seeks to invest in stocks that are deemed to be undervalued in price based on fundamental characteristics.
Contra funds will follow a contrarian investing strategy by investing in stocks that are out of favour or invest in sectors which are witnessing a slump.
A minimum of 65% of these funds are invested in equities.
Index Funds
Index funds are similar to ETFs as far as investment objective is concerned. Both are passive investments that mirror the performance of an underlying index, such as the Nifty 50 Index. The main differences being:
- Index funds are available for buying / selling at NAV based prices (end of day) but ETFs being exchange traded can be bought or sold anytime during the day.
- Index funds typically have higher expense ratios than ETFs but have lower transaction costs.
- All investments / redemptions in an index fund are settled at the NAV price but the market price of ETFs can be at a premium or discount to NAVs due to illiquidity.
- An investor can invest in index funds through SIP. However, such options are not available in ETFs as they are closed ended funds.
International Funds
These funds invest in stocks of companies located outside India. Schemes with a mandate to invest the majority of their assets in overseas markets / global commodities will form part of this category.
Debt funds are mutual funds that invest in fixed income securities like bonds and treasury bills. These are suitable for investors whose main objective is preservation of capital with stable return.
They can be further classified as:
Overnight Funds
These funds invests in bonds and money market instruments that mature in one day. They usually generate returns corresponding to the overnight rates in money markets. Probability of capital erosion is low and interest rate risk is sought to be minimized as investment is made in securities with 1 day maturity.
Liquid Funds
These funds invest in very short term debt and money market instruments. Instruments in liquid funds have a maximum maturity period of 91 days. Investors who have short term surplus cash should consider these funds as they usually offer better returns than savings bank accounts.
Ultra Short Duration Funds
These funds invest in very short term debt and money market instruments such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is between 3-6 months. They provide high degree of liquidity and stable return.
Low Duration Funds
These funds invest in very short term debt and money market instruments such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is between 6-12 months. They are preferred by investors who are willing to marginally increase their risk with an aim to earn commensurate returns. They usually generate returns a little higher than Liquid and Ultra Short Duration Funds.
Money Market Funds
These funds invest in various money market instruments having maturity upto 1 year. They are comparable to liquid funds in terms of liquidity and high quality credit rating exposure but they give the fund managers more flexibility to spread their maturity upto 1 year as per market conditions. Hence, they usually generate higher returns than liquid funds.
Short Duration Funds
These funds invest in short term bonds and money market instruments such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is between 1-3 years. As these funds have a higher maturity profile, they are more sensitive to changes in interest rates than Low Duration Funds.
Medium Duration Funds
These funds invest in medium term bonds and money market instruments such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is between 3-4 years. As these funds have a higher maturity profile, they are more sensitive to changes in interest rates than Short Duration Funds.
Medium to Long Duration Funds
These funds invest in medium term bonds and money market instruments such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is between 4-7 years. These funds tend to work well when entry and exit are timed properly as they are very sensitive to changes in interest rates.
Long Duration Funds
These funds invest in long term bonds and money market instruments such that the Macaulay duration of the portfolio is greater than 7 years. They are highly vulnerable to the changes in interest rates and are suitable for investors who have a long term investment horizon and higher risk taking ability.
Gilt Funds
These funds invest atleast 80% of their assets in government securities across maturity. These funds invest solely in high quality, low risk debt.
Gilt Funds (10 Yr Constant Duration)
These funds invest atleast 80% of their assets in government securities with an average maturity of 10 years.
Dynamic Bond Funds
They are invested in debt securities of different maturity profiles. These funds are actively managed and the portfolio varies dynamically according to the interest rate view of the fund managers.
Floater Funds
These funds invest atleast 65% of their assets in floating rate instruments. The advantage of a floating rate fund is that the fund is far less sensitive to interest rate changes, in comparison to instruments or funds which have a fixed coupon rate.
Banking & PSU Funds
These funds predominantly invest atleast 80% of their assets in debt instruments of banks, public sector undertakings and public financial institutions.
Corporate Bond Funds
These funds invest atleast 80% of their assets in highest rated corporate bonds. Maturity profile of the funds would vary as per the interest rate view of the fund managers.
Credit Risk Funds
These funds invest atleast 65% of their assets in corporate bonds below the highest rated instruments. They generate higher returns by taking higher credit risk and by investing in lower-rated papers.
FTP or FMP (Fixed Maturity Plan) Funds
These are closed ended funds with a fixed maturity date which invest in debt & money market instruments maturing on or before the date of the maturity of the scheme. The returns of FMPs are usually stable and indicative, and they carry little or no interest rate risk. These can be purchased only during its New Fund Offer (NFO).
Due to the above risk and return characteristics, FTP / FMPs are quite similar to Fixed Deposits but with tenures of over three years, they enjoy significant tax advantages over FDs, especially for investors in the highest tax bracket.
A hybrid fund is a category of mutual fund that is characterized by a portfolio which is made up of a mix of stocks and bonds, which can vary over time. These funds usually provide more stable returns than equity funds but are more volatile than debt funds.
They can be further classified as:
Equity Oriented Funds
Equity oriented funds allocate at least 65% of their portfolio into equity and the rest into debt. Equity Savings funds in this category may have a small exposure (usually around 10%) to arbitrage as well. They are taxed just like equity mutual funds.
Arbitrage Funds
An arbitrage fund is a type of mutual fund that exploits the difference in the price of a stock between cash and derivatives markets or even different stock exchanges such as the BSE and NSE. These funds are hybrid in nature as they have the provision of investing a sizeable portion of the portfolio in debt markets. However, as these funds invest predominantly in equities, their tax treatment is at par with equity funds.
Debt Oriented (Balanced) Funds
These funds invest 40%-60% of their portfolio into equity and the rest into debt. They are taxed like debt mutual funds. They usually provide higher returns than conservative hybrid funds over long holding periods. The fixed income exposure of balanced funds helps in mitigating equity-related risks.
Debt Oriented (Conservative) Funds
These funds invest 10%-25% of their portfolio into equity and 75%-90% into debt. They are taxed like debt mutual funds. These funds are ideal for investors who are looking for stable returns along with some exposure to equities.
Dynamic Asset Allocation Funds
These funds invest in both debt and equity securities which is managed dynamically. The proportion of the asset classes may change over time as per the investment objective or view of the fund manager. Most of the funds in this category maintain a minimum 65% exposure to equities and are taxed like equity oriented funds.
Multi Asset Allocation Funds
These funds invest in atleast 3 or more asset classes with a minimum allocation of 10% in each asset class. They seek to achieve capital appreciation and diversification through a mix of strategic allocation to various asset classes such as equity, debt, gold, etc. Taxation for the funds vary in this category as per their investment objective and portfolio holdings.
Solution Oriented Funds
These are open-ended schemes which have a minimum lock-in period of 5 years. These funds help for long-term goal planning. These types of schemes are particularly helpful for the investors who are willing to create their retirement or children education corpus with mutual funds. Taxation for the funds vary in this category as per their investment objective and portfolio holdings.
Retirement Funds have a lock-in period of at least 5 years or till the retirement age whichever is earlier. Children’s Funds have a lock-in period of at least 5 years or till the child attains age of majority, whichever is earlier.
Exchange traded funds are essentially index funds that are listed and traded on exchanges. An ETF is a basket of stocks or any other asset class that reflects the composition of an index. Their primary objective is to track the index return as closely as possible and reflects passive fund management.
Equity ETFs
Equity ETFs are passive investment instruments that are based on equity market indices (like Nifty 50 Index, Nifty Bank Index, etc.) and invest in securities in same proportion as the underlying index. Due to its index mirroring property, their returns usually revolve around their benchmark indices.
Debt ETFs
Debt ETFs are passive investment instruments that invest in various debt instruments like treasury bills, government securities, call money, etc.
Gold ETFs
Gold ETFs are exchange traded funds where the underlying asset is gold. Therefore, value of gold ETF depends upon the price of gold.
Gold Mutual Funds
These are mutual funds which invest in various forms of gold. It can be in the form of Gold ETFs or stocks of gold mining companies.
Fund of Funds Domestic
These funds invest in various domestic mutual funds rather than investing directly in any asset class. Minimum 95% of the total assets are invested in various domestic funds. It usually provides greater diversification than traditional Mutual Funds by spreading investors’ money across different investing styles.
Fund of Funds Overseas
These funds invest in various overseas mutual funds rather than investing directly in any asset class. Minimum 95% of the total assets are invested in various global funds. Equity Fund of Funds tax treatment is a major disadvantage to the investors as they are taxed like Non-equity funds, even though they may be invested in only equity funds.
To explore the top performing mutual funds in any category, please use our Mutual Fund Screener.